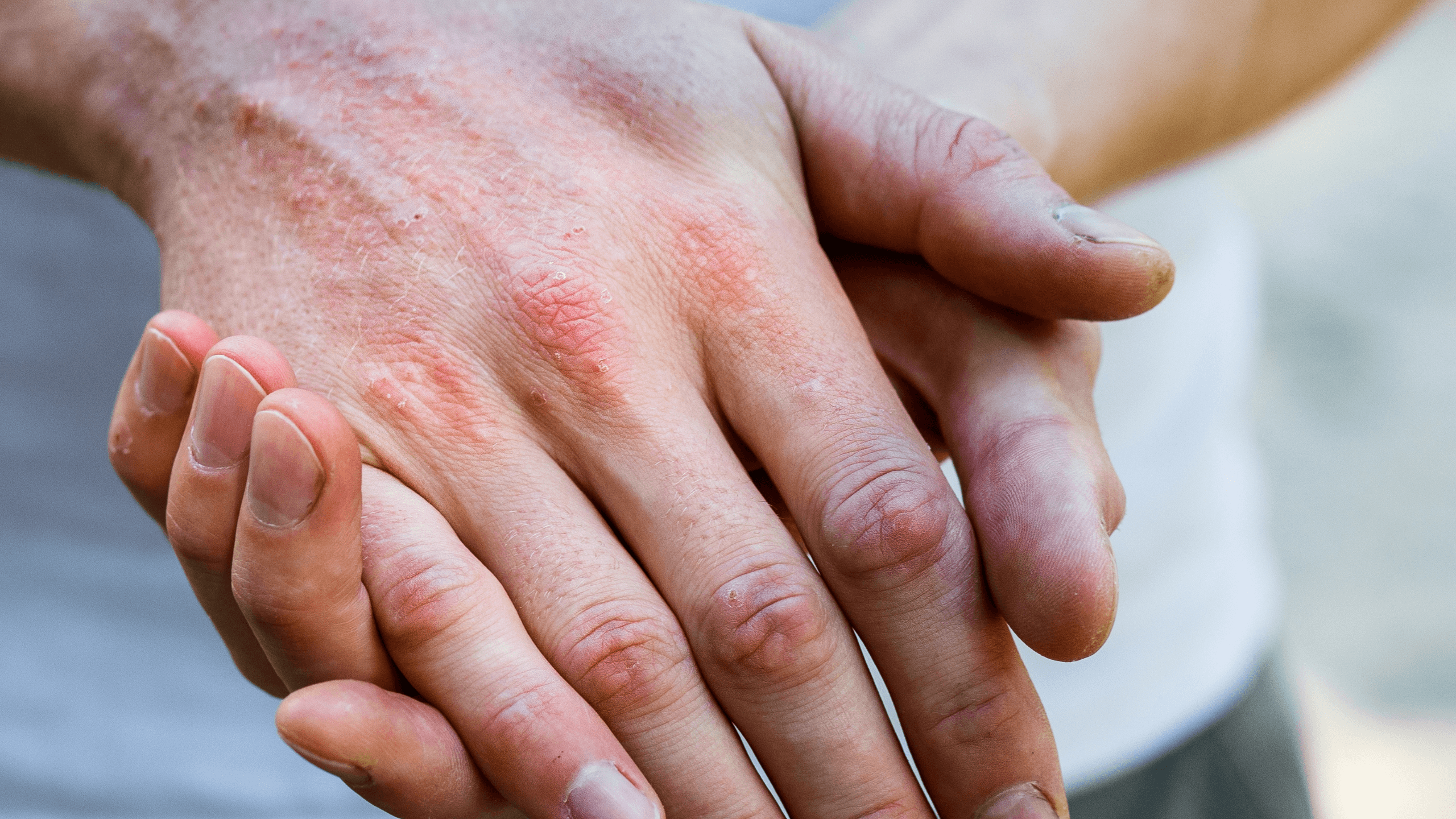
10% of the U.S. population has some form of eczema–and there’s no easy answer about how long it lasts. While we can’t tell you when or if you’ll be free of eczema, we can help you understand eczema stages, types, triggers, and treatments, all of which influence the course of the condition.
Will Eczema Go Away on Its Own?
Eczema often won’t go away on its own, and it shouldn’t be left untreated. While there is no cure for eczema, there are treatments that can minimize flare-ups and ease symptoms. Eczema can and does recur. While adult eczema most likely won’t go away on its own, eczema in children can resolve over time. 60% of people who have experienced eczema developed it in infancy. Of those people, an estimated 67% will outgrow the skin condition.
How Long Will an Eczema Flare-Up Last?
How long a specific eczema flare-up will last depends on the type of eczema, its severity, and the health of the skin and its microbiome.
When experiencing atopic dermatitis, the general form of eczema most of us are more familiar with, your flare-ups may last longer than some other forms of eczema. That’s because the underlying cause of atopic dermatitis is mostly unknown. It could be a result of genetics, an imbalance in the skin microbiome, inflammation, immune system malfunction, or other factors.These complicated underlying causes can make atopic dermatitis difficult to understand and manage.
The 3 Stages of Eczema
Depending on the frequency, severity, and duration of your rash, your eczema may be classified as being in one of these three stages:
Acute refers to an eczema rash that has just appeared. When you think of a flare-up, you’re likely picturing the acute stage of eczema. The symptoms and pain are often most intense during this stage. Think: intense itchiness, redness, bumps, and swelling.
Subacute is the stage between chronic and acute. It’s the middle stage when you may be experiencing symptoms like flaking and cracks of the skin, but don’t have the same intense itching as the acute stage. This is often the phase you move into as you’re healing from a flare-up.
Chronic is the most common stage. It’s eczema that develops and stays around a while. Many people with chronic eczema develop it as an infant and have on-and-off symptoms throughout childhood. Many adults have chronic eczema as well. Symptoms of chronic eczema include itching, thickening of the skin, discoloration, and cracking of the skin.
What Gets Rid of Eczema Fast?
Just like you, we wish there was a one-size-fits-all way to treat eczema. While there’s no cure, there are steps you can take to help reduce eczema symptoms as quickly as possible:
Avoid Triggers
While environmental factors may not be the root cause of your atopic dermatitis, they can trigger eczema flare-ups. Common culprits include:
- Household items such as detergents and cleaners
- Airborne allergens
- Dust mites
- Stress
- Fragrances
- Wool clothing
- Extreme weather, such as very dry air or severe cold
- Foods, including undiagnosed food allergies
Identifying your eczema triggers is hard. Many people with eczema don’t know their triggers. However, you can try determining which of these factors influence your flare-ups by keeping a close eye on your symptoms and journaling where you’ve been, what you’ve done, what you’ve eaten, and what the weather’s been like before and at the start of your flare-up.
Avoiding triggers probably won’t make your eczema go away completely, but minimizing exposure may help lessen the severity and frequency of your flare-ups.
Consult Your Dermatologist
Consulting with a board-certified dermatologist is the best way to receive an accurate diagnosis and determine the eczema treatments that are best for you.
After examining your skin and determining the severity of your skin condition, a dermatologist may recommend:
- A topical corticosteroid
- A calcineurin inhibitor (such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus)
- Antihistamines to help reduce itch
- Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitors (such as Eucrisa)
If you’re considering using a topical corticosteroid (also simply called “steroids”), remember that long-term use can result in unwanted side effects, including topical steroid withdrawal.
Balance the Skin Microbiome
While the exact cause of eczema remains unknown, doctors and researchers believe Staph A. bacteria (scientifically known as Staphylococcus aureus) may trigger an overreaction of the immune system that results in higher levels of inflammation.
Hundreds of eczema creams and lotions fill the store shelves with the goal of bringing moisture back to the skin, but few target imbalances in the skin microbiome.
Gladskin Eczema Cream uses Micreobalance®, a patented smart protein, to restore balance to the skin microbiome gently and effectively while moisturizing at the same time. Formulated without resistance-causing or harsh ingredients, it works with your body instead of against it.
Free of steroids, fragrances, drying alcohols, preservatives, parabens, and sulfates, our Eczema Cream is clinically tested and safely formulated for anyone three months and up.
The best part? Four out of five users have reduced itch and redness from using the Gladskin Eczema Cream. You can too — learn more.
Managing Eczema Over Time
How long does eczema last? We can’t say for certain. Eczema could be something you work to manage throughout your lifetime. But with proper care, you can minimize symptoms and reduce the frequency of flare-ups.
By addressing a possible imbalance in the skin microbiome, you can experience even more relief from the itchiness and dryness associated with eczema, because you’re working to help correct one of the possible causes.