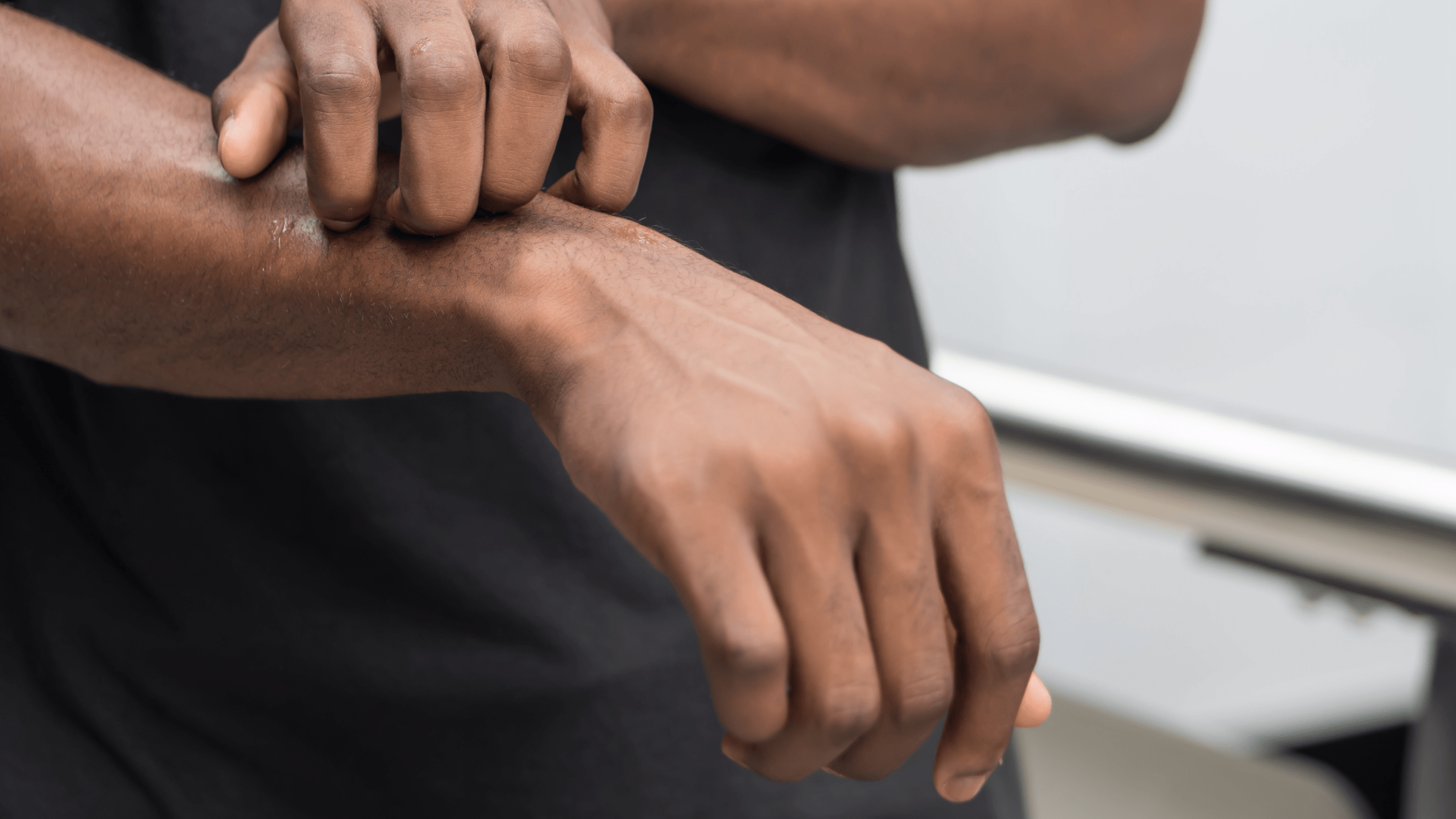
Eczema causes red, itchy, dry, and flaky skin, yet the severity of eczema can range from mild to severe.
If you’re suffering from severe eczema, chances are you’ll know it. Severe eczema can cause sleeplessness, embarrassment, and distress due to the discomfort of the skin condition… but sometimes the same holds true for mild eczema, too.
So how do you tell the difference between mild vs. severe eczema? Well, it turns out doctors have a few different indexes to help analyze the severity of eczema, also called atopic dermatitis.
How to Measure Eczema Severity
The most popular methods of measuring the severity of eczema are the Severity Scoring of Atopic Dermatitis Index (SCORAD) and the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI).
The SCORAD analyzes the area and intensity of eczema to determine its severity. The index weighs the size and the location of eczema accordingly, depending on whether it appears on the head and neck, upper limbs, lower limbs, trunk, genitals, or back.
It then evaluates the intensity, based on redness, oozing, swelling, thickening skin, scratch marks, and dryness.
Like the SCORAD, the EASI also looks at the location and intensity of eczema to determine its severity.
The EASI breaks the body into four regions: the head/neck, trunk, upper limbs, and lower limbs. It then looks at the intensity of redness, scratch marks, thickening and papulation (the formation of small, raised bumps), as well as lichenification (when your skin becomes thick and leathery).
Each index has its own set of calculations to determine a severity score.
These indexes can be helpful for doctors to evaluate eczema severity, because they’re objective; however, research shows that patients and doctors often rate the severity of their skin condition quite differently.
What does that mean? Well, even if a doctor determines your eczema is mild, that doesn’t diminish the psychological, social, and physical effects it’s having in your life.
Mild vs. Severe Eczema: 6 Signs Your Eczema May Be Severe
If you don’t want to evaluate your eczema based on numbers and formulas, we get it. Here are a few common symptoms of eczema that’s more severe.
If you’re experiencing any of these signs and symptoms with your atopic dermatitis, it may be an indication your skin condition has progressed past the mild stage.
Uncontrollable Itching and/or Bleeding
When you scratch your skin so often, or so harshly, that it opens the skin and begins to bleed, this indicates potentially severe eczema. Open wounds in the skin increase your risk of infection and pose a greater threat to your overall skin health.
Blistering
Blisters are another symptom of severe eczema. Oftentimes when someone experiences occasionally itchy, mild atopic dermatitis, no blisters will be present.
However, when blisters form and ooze fluid, this is often considered severe. Be aware that there are other types of eczema that more frequently cause blisters, such as dyshidrotic eczema.
Thick Patches of Skin
Both the SCORAD and EASI evaluate thickening skin as a sign of severe eczema. Often, when eczema is very itchy, scratching will cause patches of skin to thicken over time. These raised patches may also appear leathery — and may even feel leathery, too.
Larger Areas of Redness
Both the SCORAD and EASI take into account the location and area of your eczema patches. Typically, when your red, itchy eczema takes up more surface area of the skin, it increases the perceived intensity of the skin condition.
However, maybe you know from experience that sometimes the rashes that look the least severe are really the itchiest and most bothersome. So just because your rash is small, the itching and the annoyance may be big.
Ineffective Treatment
Mild cases of eczema typically respond well to topical treatments such as ointments and creams. Your doctor may even have prescribed a topical corticosteroid (although be aware of topical steroid withdrawal).
If these topical treatments aren’t reducing your eczema symptoms, this may be an indication you’re suffering from severe atopic dermatitis. Your doctor may begin discussing injections and oral medications as options for the next level of treatment. Light therapy is another option for severe eczema.
If you haven’t done so already, check out Gladskin Eczema Cream. Four out of five users experience reduced itch and redness associated with eczema — and best of all, it targets a cause of the skin condition: an imbalanced skin microbiome.
Losing of Sleep
Constant itching can lead to a serious loss of sleep. Itchy skin can leave you tossing and turning in bed, scratching.
If your eczema is causing a loss of sleep, your condition may be considered severe. If you haven’t yet talked to your healthcare provider about your skin, now’s the time. Losing sleep can have a detrimental effect on your overall quality of life.
Conclusion
Whether your eczema is mild, severe, or somewhere in between, it’s important to establish a treatment plan with your primary healthcare provider and stick with it.
Many people find relief from eczema symptoms through avoiding both hot showers and overwashing, moisturizing frequently, minimizing exposure to harsh skin care ingredients, and implementing lifestyle tips to rebalance your skin microbiome.
When in doubt, Gladskin Eczema Cream reduces itch and redness in 80% of users. Learn more.