Chances are when you think of rosacea, you think of a singular chronic skin condition that causes redness and flushing on the face. However, there are actually four distinct types of rosacea.
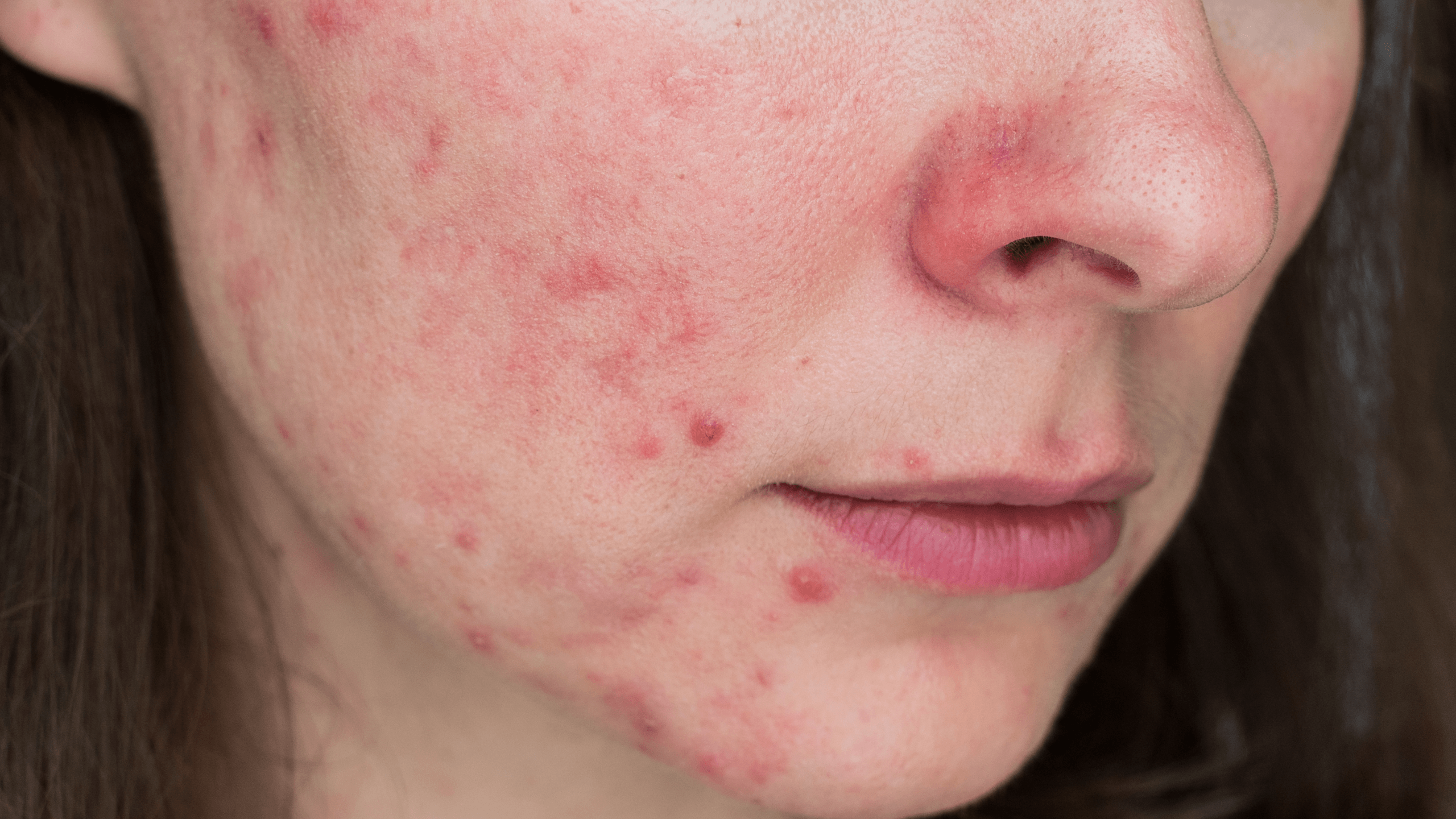
Understanding Papulopustular RosaceaPapulopustular rosacea is a type of rosacea that causes acne-like symptoms. The most distinct symptom is pus-filled bumps called papules and pustules that generally appear on the forehead and cheeks. They develop deep within the skin, which makes them difficult to get rid of. Papulopustular rosacea is also called subtype 2 rosacea.
Because papulopustular rosacea looks so much like acne, it’s important to understand the difference between the two conditions. Mixing up acne and papulopustular rosacea can actually lead to worsening symptoms! Acne treatment won’t work on papulopustular rosacea and can even make it worse.
So, let’s uncover what exactly papulopustular rosacea looks like, how it compares to acne, and how to treat it.
What Are the Symptoms of Papulopustular Rosacea?
The symptoms of papulopustular rosacea are quite similar to what you’d think of as standard rosacea symptoms. When most people think of rosacea, they picture what’s called erythematotelangiectatic rosacea, or ETR.
Papulopustular rosacea can cause the same symptoms, like flushed skin, a burning or stinging sensation, and visible blood vessels — but also includes the key pus-filled bumps.
These symptoms typically appear on the forehead, cheeks, chin, and nose.
What Causes Papulopustular Rosacea?
The exact cause of rosacea is still unknown. However, we do know some factors that can contribute to rosacea, including:
- Genetics
- Environment
- Skin mites
- Poor gut health
- Inflammation
- An imbalance of the skin microbiome
Interestingly enough, researchers believe that skin mites themselves don’t contribute to rosacea — but the bacteria that they carry do. That means an imbalance of bad bacteria to good bacteria in the skin microbiome likely accounts for more cases of rosacea than we even realize today.
What Triggers Papulopustular Rosacea?
Papulopustular rosacea triggers will vary from person to person, but there are some common trends doctors and researchers have observed among rosacea sufferers. Common papulopustular rosacea triggers include:
- Emotional stress and anxiety
- Spicy foods
- Alcohol
- Hot beverages
- Extreme heat (weather, hot baths and showers, saunas, etc.)
- Extreme cold
- Strong winds
- UV rays
- Physical exertion
- Foods high in histamines
According to the National Rosacea Society, even non-spicy foods like yogurt, liver, and sour cream can act as rosacea triggers.
What Are the Differences Between Papulopustular Rosacea and Acne?
Both papulopustular rosacea and acne are similar-looking skin conditions. In fact, papulopustular rosacea is sometimes confusingly referred to as ‘acne rosacea.’ However, these two conditions aren’t related. The use of the term acne rosacea can lead people to believe they have acne in addition to rosacea. However, acne and rosacea are two distinct conditions that need to be identified as such.
One of the key differences between papulopustular rosacea and acne are the treatment methods. Using acne treatment on papulopustular rosacea can actually make the condition worse. That’s why receiving a proper diagnosis should be your first priority when you discover any new bumps on your skin.
Another distinct difference between acne and rosacea are blackheads. Blackheads aren’t a symptom of papulopustular rosacea. They’re only a symptom of acne. On the other hand, persistent redness is primarily a symptom of rosacea, but it can be present to some degree with acne. You can also experience redness if you’re using a harsh acne treatment that is drying out your skin.
Likewise, rosacea is often associated with dry skin, while acne is more likely to be associated with oily skin. Overly harsh acne treatments can dry out the skin. Before determining whether your skin is naturally oily or dry, consider the products in your skin care routine.
At the end of the day, to make the proper diagnosis between papulopustular rosacea and acne, you’ll need to visit the dermatologist. Both skin conditions can cause red, bumpy skin. The untrained eye won’t likely be able to distinguish between the two.
How Is Papulopustular Rosacea Treated?
Because there is no cure for rosacea (yet!), treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving your overall quality of life. Here are several ways you can begin improving facial redness and eliminate pesky pustules:
Protecting Your Skin From the Sun
61% of people with rosacea rank sun exposure as their biggest rosacea trigger. UV rays cause the growth of new blood vessels, which increases facial redness and flushing severity. A rise in body temperature from the sun and any physical exertion while outdoors can also increase your risk of a rosacea flare-up.
To help protect your skin from the powerful UV rays, stay in the shade when possible and avoid the harshest hours of sunlight during the day (between 10am and 2pm).
For the best protection, apply a rosacea-friendly sunscreen that has 30+ SPF. The best sunscreens for flushed, sensitive skin are made with zinc oxide and/or titanium dioxide and are free of chemicals like oxybenzone, avobenzone, octisalate, octocrylene, homosalate, octinoxate, and fragrances.
Identifying and Avoiding Triggers
To determine your personal rosacea triggers, work with your health care provider and keep a journal to note where you’ve been, what you’ve eaten, or what you’ve been exposed to when you experience a rosacea flare-up. This will help you better track trends and decipher what’s causing your redness and bumps to worsen.
When you’re first trying to identify your triggers, remember to be patient and kind to yourself. This can be a tough and long process, which is why it’s so much better to partner with your doctor to help you narrow down your personal rosacea triggers.
The best part is, once you’ve identified your personal triggers, avoiding them will likely significantly improve your rosacea symptoms.
Choose Gentle Skin Care
With facial redness, hypoallergenic and fragrance-free products are the way to go. Certain ingredients and chemicals in skincare can irritate the skin and make facial redness worse.
Avoid skin care products containing:
- Drying alcohols
- Camphor
- Fragrance
- Glycolic acid
- Lactic acid
- Menthol
- Sodium laurel sulfate
- Urea
Instead, look for a gentle moisturizer, face wash and makeup remover that are formulated with minimal ingredients.
Visiting Your Dermatologist
If you have papulopustular rosacea, talk to your dermatologist about treatment options. Everyone’s skin is unique, and your dermatologist can provide a personalized papulopustular rosacea treatment plan. If your skin isn’t responding to topical treatments or lifestyle changes, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. Talk to your doctor about safe antibiotics use, the impact of antibiotics on the microbiome and how to minimize side effects.
Your doctor may also recommend laser or light therapy. This therapy uses pulses of light to reduce the size of blood vessels in your face and lower inflammation, itchiness, and irritation. Laser therapy is often needed on a recurring basis to experience the full benefits.
At the end of the day, speak with your doctor and dermatologist about how best to treat your papulopustular rosacea. They’ll be able to see your skin and discern what’s best for you in the short- and long-term.
Balancing the Skin Microbiome with Gladskin's Redness Relief Cream with Micreobalance ®
Research shows that the skin microbiomes of people with persistent facial flushing and redness are very different from the skin microbiomes of those with healthy skin.
Gladskin’s Redness Relief Cream with Micreobalance® reduces the appearance of facial redness, leading to calmer-looking skin. It balances the skin microbiome as it moisturizes and is free of antibiotics, vasoconstrictors, and parasiticides. Learn more here.